Did you know we have a monthly newsletter? View past volumes and subscribe.
Machine learning tool fills in the blanks for satellite light curves
Feb. 13, 2024 -
When viewed from Earth, objects in space are seen at a specific brightness, called apparent magnitude. Over time, ground-based telescopes can track a specific object’s change in brightness. This time-dependent magnitude variation is known as an object’s light curve, and can allow astronomers to infer the object’s size, shape, material, location, and more. Monitoring the light curve of...
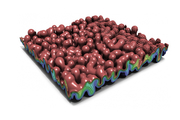
Will it bend? Reinforcement learning optimizes metamaterials
Dec. 13, 2023 -
Lawrence Livermore staff scientist Xiaoxing Xia collaborated with the Technical University of Denmark to integrate machine learning (ML) and 3D printing techniques. The effort naturally follows Xia’s PhD work in materials science at the California Institute of Technology, where he investigated electrochemically reconfigurable structures. In a paper published in the Journal of Materials...
LLNL’s Kailkhura elevated to IEEE senior member
Nov. 8, 2023 -
IEEE, the world’s largest technical professional organization, has elevated LLNL research staff member Bhavya Kailkhura to the grade of senior member within the organization. IEEE has more than 427,000 members in more than 190 countries, including engineers, scientists and allied professionals in the electrical and computer sciences, engineering and related disciplines. Just 10% of IEEE’s...
LLNL, University of California partner for AI-driven additive manufacturing research
Sept. 27, 2023 -
Grace Gu, a faculty member in mechanical engineering at UC Berkeley, has been selected as the inaugural recipient of the LLNL Early Career UC Faculty Initiative. The initiative is a joint endeavor between LLNL’s Strategic Deterrence Principal Directorate and UC national laboratories at the University of California Office of the President, seeking to foster long-term academic partnerships and...
Explainable artificial intelligence can enhance scientific workflows
July 25, 2023 -
As ML and AI tools become more widespread, a team of researchers in LLNL’s Computing and Physical and Life Sciences directorates are trying to provide a reasonable starting place for scientists who want to apply ML/AI, but don’t have the appropriate background. The team’s work grew out of a Laboratory Directed Research and Development project on feedstock materials optimization, which led to...
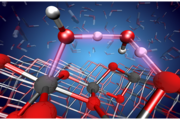
Machine learning reveals refreshing understanding of confined water
July 24, 2023 -
LLNL scientists combined large-scale molecular dynamics simulations with machine learning interatomic potentials derived from first-principles calculations to examine the hydrogen bonding of water confined in carbon nanotubes (CNTs). They found that the narrower the diameter of the CNT, the more the water structure is affected in a highly complex and nonlinear fashion. The research appears on...
Consulting service infuses Lab projects with data science expertise
June 5, 2023 -
A key advantage of LLNL’s culture of multidisciplinary teamwork is that domain scientists don’t need to be experts in everything. Physicists, chemists, biologists, materials engineers, climate scientists, computer scientists, and other researchers regularly work alongside specialists in other fields to tackle challenging problems. The rise of Big Data across the Lab has led to a demand for...
Fueling up hydrogen production
April 3, 2023 -
Through machine learning, an LLNL scientist has a better grasp of understanding materials used to produce hydrogen fuel. The interaction of water with TiO2 (titanium oxide) surfaces is especially important in various scientific fields and applications, from photocatalysis for hydrogen production to photooxidation of organic pollutants to self-cleaning surfaces and biomedical devices. However...
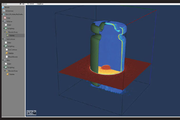
From plasma to digital twins
March 13, 2023 -
LLNL's Nondestructive Evaluation (NDE) group has an array of techniques at its disposal for inspecting objects’ interiors without disturbing them: computed tomography, optical laser interferometry, and ultrasound, for example, can be used alone or in combination to gauge whether a component’s physical and material properties fall within allowed tolerances. In one project, the team of NDE...
New HPC4EI project to create 'digital twin' models for aerospace manufacturing
Jan. 19, 2023 -
A partnership involving LLNL aimed at developing “digital twins” for producing aerospace components is one of six new projects funded under the HPC for Energy Innovation (HPC4EI) initiative, the Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy announced. Sponsored by the HPC4Manufacturing (HPC4Mfg) Program, one of the pillars of HPC4EI, the collaboration between LLNL...
Cognitive simulation supercharges scientific research
Jan. 10, 2023 -
Computer modeling has been essential to scientific research for more than half a century—since the advent of computers sufficiently powerful to handle modeling’s computational load. Models simulate natural phenomena to aid scientists in understanding their underlying principles. Yet, while the most complex models running on supercomputers may contain millions of lines of code and generate...
ML model instantly predicts polymer properties
Nov. 30, 2022 -
Hundreds of millions of tons of polymer materials are produced globally for use in a vast and ever-growing application space with new material demands such as green chemistry polymers, consumer packaging, adhesives, automotive components, fabrics and solar cells. But discovering suitable polymer materials for use in these applications lies in accurately predicting the properties that a...
LLNL researchers win HPCwire award for applying cognitive simulation to ICF
Nov. 17, 2022 -
The high performance computing publication HPCwire announced LLNL as the winner of its Editor’s Choice award for Best Use of HPC in Energy for applying cognitive simulation (CogSim) methods to inertial confinement fusion (ICF) research. The award was presented at the largest supercomputing conference in the world: the 2022 International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking...
Understanding the universe with applied statistics (VIDEO)
Nov. 17, 2022 -
In a new video posted to the Lab’s YouTube channel, statistician Amanda Muyskens describes MuyGPs, her team’s innovative and computationally efficient Gaussian Process hyperparameter estimation method for large data. The method has been applied to space-based image classification and released for open-source use in the Python package MuyGPyS. MuyGPs will help astronomers and astrophysicists...
Papers win Test of Time awards at 2022 IEEE VIS conference
Oct. 31, 2022 -
Two LLNL-led teams received SciVis Test of Time awards at the 2022 IEEE VIS conference on Oct. 18, for papers that have achieved lasting relevancy in the field of scientific visualization. Published in 2008, an LLNL-led paper that—for the first time—allowed Digital Morse Theory to be applied to large scale and three-dimensional data, won the 14-year Test of Time award for making a lasting...
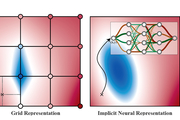
Project co-led at LLNL looks to improve visualization of largescale datasets
Oct. 27, 2022 -
LLNL researchers are starting work on a three-year project aimed at improving methods for visual analysis of large heterogeneous data sets as part of a recent Department of Energy funding opportunity. The joint project, entitled “Neural Field Processing for Visual Analysis,” will be led at LLNL by co-principal investigator (PI) Andrew Gillette. Gillette is joined by lead PI Matthew Berger at...
LLNL to cooperate with University of Utah's one oneAPI Center of Excellence
Sept. 21, 2022 -
The University of Utah has announced the creation of a new oneAPI Center of Excellence focused on developing portable, scalable and performant data compression techniques. The oneAPI Center will be headed out of the University of Utah’s Center for Extreme Data Management Analysis and Visualization (CEDMAV) and will involve the cooperation of LLNL’s Center for Applied Scientific Computing. It...
Assured and robust…or bust
June 30, 2022 -
The consequences of a machine learning (ML) error that presents irrelevant advertisements to a group of social media users may seem relatively minor. However, this opacity, combined with the fact that ML systems are nascent and imperfect, makes trusting their accuracy difficult in mission-critical situations, such as recognizing life-or-death risks to military personnel or advancing materials...
CASC team wins best paper at visualization symposium
May 25, 2022 -
A research team from LLNL’s Center for Applied Scientific Computing won Best Paper at the 15th IEEE Pacific Visualization Symposium (PacificVis), which was held virtually on April 11–14. Computer scientists Harsh Bhatia, Peer-Timo Bremer, and Peter Lindstrom collaborated with University of Utah colleagues Duong Hoang, Nate Morrical, and Valerio Pascucci on “AMM: Adaptive Multilinear Meshes.”...
Paving the way to tailor-made carbon nanomaterials and more accurate energetic materials modeling
March 17, 2022 -
To better understand how carbon nanomaterials could be tailor-made and how their formation impacts shock phenomena such as detonation, LLNL scientists conducted machine-learning-driven atomistic simulations to provide insight into the fundamental processes controlling the formation of nanocarbon materials, which could serve as a design tool, help guide experimental efforts and enable more...